54 yo female is admitted to the hospital with CC: SOB x 2 days. She complains of cough with wheezing, and denies chest pain, fever or chills.
PMH: COPD/asthma, HTN, hypothyroidism
Medications: Aspirin, Lasix, Maxzide, albuterol, Synthroid
Allergies: PCN
SH: Smoker, denies alcohol or illicit drug use
Physical exam:
VS 36.3-22-60-118/86
Chest: decreased air movement (B) with wheezing
CVS: Clear S1S2
Abd: Soft, NT
Labs:
ABG on 4 L/min revealed a pH of 7.39, pCO2 53, pO2 68, SpO2 89
CXR: Scoliosis, cardiomegaly, atelectasis, and pleural scarring
EKG: NSR
What happened?
Patient was given breathing treatments with albuterol and Atrovent, terbutaline 0.3 mg SQ x 2, Solu-Medrol 60 mg IV and magnesium 2 g at 100 ml of saline over one hour.
After treatments, the patient is saturating at 78% to 80% on RA. She was admitted for treatment of COPD exacerbation.
CBC showed polycythemia - Hgb 20, Hct 60

CBC in polycythemia
What tests should you order in the work-up of polycythemia?
Check SpO2, ABG, Epoetin level, B12 and AP
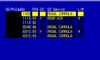


SpO2 and ABG in secondary polycythemia


CMP, B12; Epo level is very high
Final diagnosis: Polycythemia secondary to hypoxemia due to COPD
What happened next?
Patient's SOB improved with COPD therapy. Her Hct decreased with gentle hydration, and she was discharged home with home O2 and follow-up with her PCP in 2 weeks.

COPD treatment, note the nicotine patch
What did we learn from this case?
Polycythemia can be one of two types: primary (a true bone marrow disorder) and secondary.
Secondary polycythemia is much more common and is due to heavy smoking (elevated carboxyhemoglobin), COPD or dehydration. Our patient's condition is due to smoking and low SpO2 due to COPD.
Polycythemia vera is diagnosed by using the Polycythemia Vera Study Group major criteria: elevated red blood cell mass (not a practical test, rarely done), SpO2 > 92%, and palpable splenomegaly (3 major criteria).
Polycythemia rubra vera (PRV) is an autonomous RBC proliferation (not dependent on erythropoetin), and epoetin level is low or normal. Low EPO level has 70% sensitivity and 90% specificity for polycythemia vera.
Other lab findings in PRV (minor criteria):
Platelets > 400
WBC> 12
High leucocyte alk phos (LAP)> 100, DDx with CMP in which LAP is low
High B12> 900
Low MCV
PRV is a part of the myeloproliferative disorders, remembered by the mnemonic MEPC:
Myelofibrosis
Essential Thrombocythemia
PRV
CML
References:
Polycythemia Vera - AFP 05/04
Polycythemia Vera (Primary Polycythemia; Vaquez' Disease) - Merck Manual
Polycythemia Vera - eMedicine

No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.