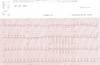
EKG of atrial fibrillation
CHADS2 score was included in the ACC/AHA/Physician Consortium 2008 Clinical Performance Measures for Adults With Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation or Atrial Flutter. Patients with a score greater than one typically are treated with warfarin.
MDCalc has an online calculator for CHADS2.
Generally, I find mnemonics useful and have listed some that I made up when studying for USMLE and ABIM at Medical Mnemonics. There are more than 1,000 mnemonics in my database and I hope to publish them online one day in not too distant future.
NorthShore University HealthSystem Cardiac Electrophysiologists Wes Fisher, M.D., Jose Nazari, M.D. and Alex Ro, M.D. discuss atrial fibrillation.
References:
Senator Warner Has Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence. Dr. Wes.
Should patients receive anticoagulation for paroxysmal atrial flutter?
Radiofrequency Ablation as First-Line Treatment for AFib
AFib with RVR after a TLC Placement
How to Score Well on the Boards?
Medical Mnemonics
Updated: 08/11/2009


